Adaptive Q-Learning for Fair and Dynamic Server Selection in Edge Computing: Addressing Latency Variability in Real-Time Applications
Keywords:
Edge Computing, Adaptive Q-Learning, Server Selection, Cloud Gaming, Latency Variance, FairnessAbstract
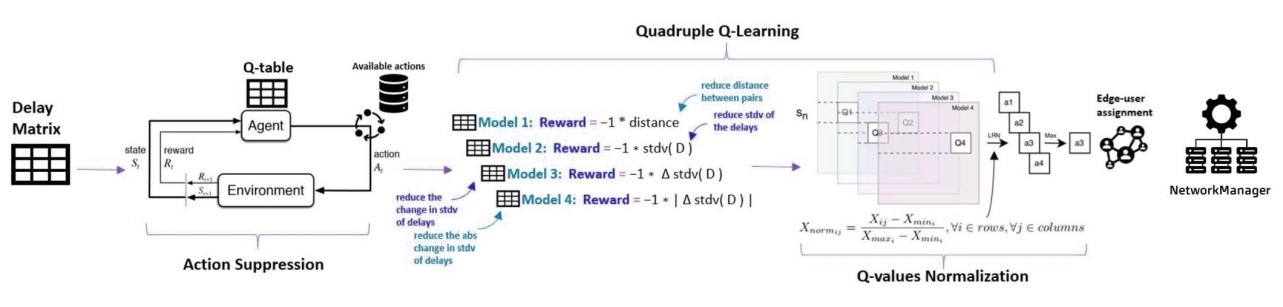
The main purpose of edge computing is to provide real-time services, such as cloud gaming and virtual collaboration, which are closer to users thereby reducing latency. However, dynamically pairing users with appropriate edge servers becomes an increasing problem due to a changing and adaptable network environment and different latency requirements from different applications. To address this challenge, we propose a novel Adaptive Q-Learning algorithm for fair server selection while maintaining low variation in latency. The core of our approach involves enhancing the Quadruple Q-Learning model. Our model has been equipped with dynamic action suppression mechanisms that are changed by the most recent network performance indicators. Conventional Q-learning approaches typically make the error of not examining the current load on the nearest server, which can cause some users’ resources to saturate and increase their latencies. With normalization of Q-values and a flexible learning rate, our algorithm adjusts better when network latencies change, packets are lost or servers become congested. We strive for more balanced traffic distribution across nodes by achieving equitable user requests spread across the network; thus preventing any one service node from becoming overwhelmed. Through simulations in a cloud gaming context, we demonstrate that our proposed Adaptive Q-Learning method outperforms existing algorithms.Our method however is not only capable of holding strictly to such latency thresholds. Besides, it is also functional in implementing fairness so all users may experience similar latency levels. The article emphasizes the necessity of adaptive and impartial server selection in edge computing environments to make the time-critical applications more user-friendly.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.


