An Enhanced Textual Review Classification and Sentiment Analysis Approach based on Machine Learning: A Comprehensive Analysis for Text Categorization Approaches
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62019/x6sz1d43Abstract
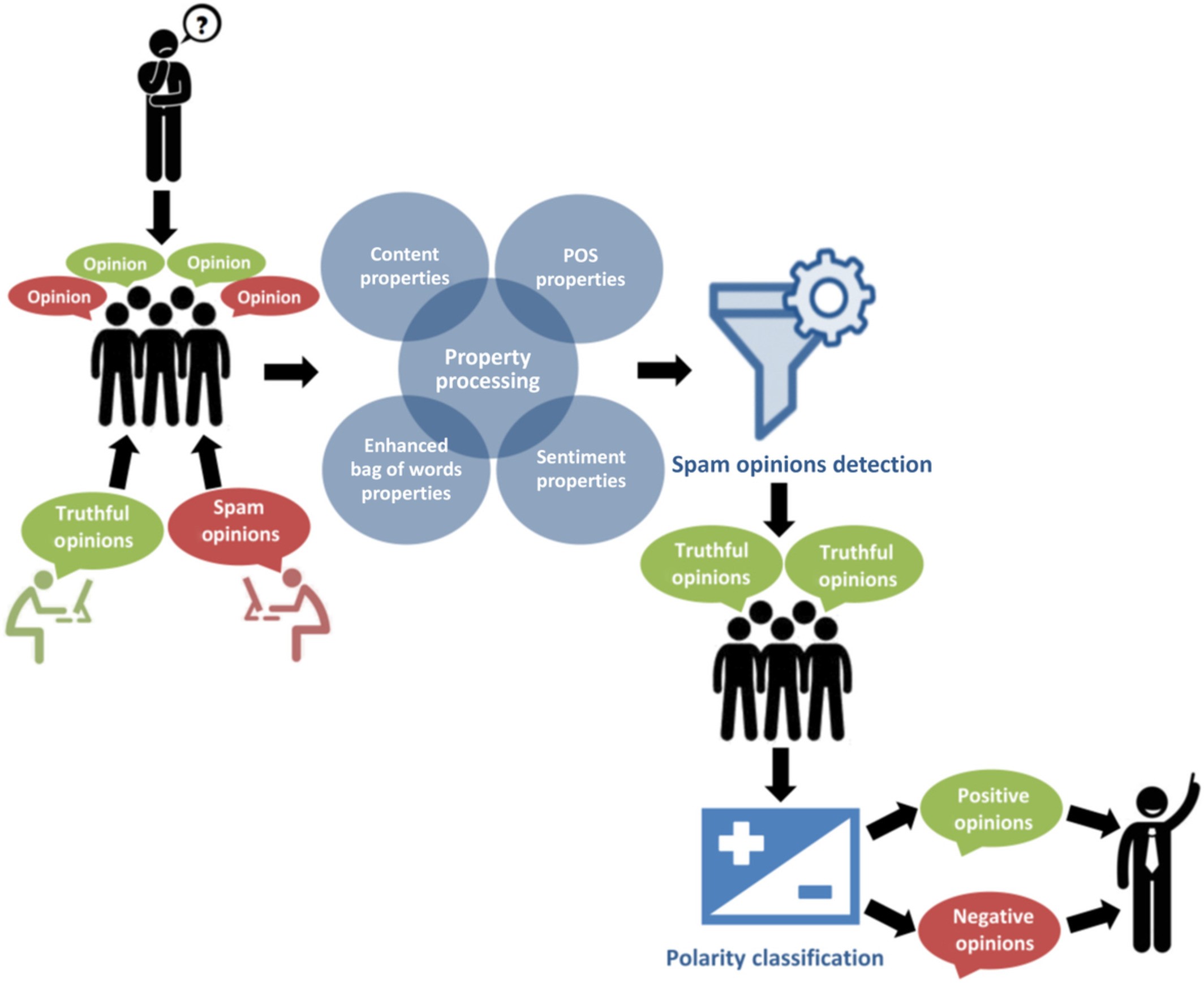
Since interpretable feature-engineered pipelines, natural language processing (NLP) has developed into deep neural and transformer-based architectures, and finally, large language models (LLMs) that can generalize their results across tasks. This development has significantly enhanced the subjective language comprehension, such as sentiment, emotion, sarcasm, humor, stance, metaphor, intent and aesthetic judgments, and increased the requirements of explainability in high-stakes areas. Already trained transformers (e.g., encoder-only and decoder-only versions) and LLMs like BERT and GPT have established powerful baselines on text classification and zero/few-shot subjectivity modeling, but the opaqueness of these models drives language-based rationalization (extractive/abstractive natural-language justifications) and feature-attribution algorithms (e.g., LIME, Integrated Gradients, SHAP). The four strands brought together by this survey include: (i) sentiment-analysis methods and datasets (e.g., IMDb, Sentiment140, Twitter Airline, SemEval), (ii) transformer-era text classification, (iii) LLMs on subjective language, and (iv) rationalization of explainable NLP. We have provided a unified taxonomy of subjective tasks and have analyzed model families, starting with classical ML up to transformers/LLMs; have collected major data sets and benchmarks; and have systematized explainability methods, in particular rationalization, and their evaluations and classify open problems dataset bias and annotation ambiguity, constraints of faithfulness and explanatory comprehensibility, evaluation bias, compute cost, and ethical risks. The article will facilitate the formation of a coherent foundation of explainable, credible subjective NLP based on the functions of transformer/LLM and analyze feature extraction techniques methodically based on LLM. We have trained a Machine Learning classifier using 70% of the training data and 30% of the testing data. Based on our results, we find that the proposed ML based technique gives enhanced performance, with an improved accuracy of 99% in the UCI-ML reviews dataset and 96% in the Twitter Kaggle dataset. This study underscores the paramount significance of feature extraction in sentiment analysis, endowing pragmatic insights to elevate model performance and steer future research pursuits.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ali Ahmed, Nasar Ahmed, Umair Ghafoor, Syed Muhammad Rizwan , Rizwan Qureshi , Hamayun Khan , Muhammad Zunnurain Hussain

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.






