An Exploration of User-level Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning Technique: A Machine Learning Perspective on Classification, Threat Mitigations, and Exploring Federated Learning and Beyond
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62019/5n05ms49Abstract
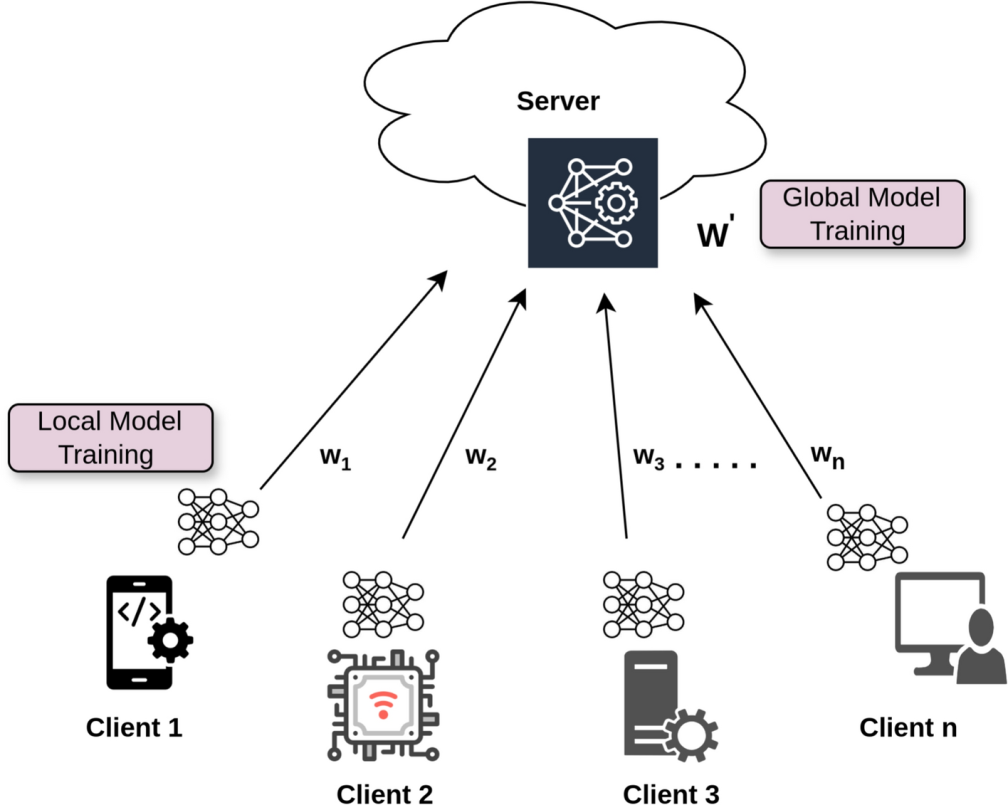
The federated learning (FL) concept makes sure that a machine learning model is created by multiple clients without them sharing their local data. The prohibition policies of data exchange among organizations provided by various governments have resulted in the necessity of privacy-preserved federated learning. Federated learning has developed this concept of modeling development in many industries to improve performance and accuracy. The following paper provides the classification of Federate Learning, covering the presence of aggregation algorithms, frameworks, aspects of implementation, and dataset repositories, making it a crucial source of information to researchers working in the area. The paper critically examines the available centralized and decentralized FL methods that have been proposed in the literature and provides an overview regarding the methodology, privacy techniques applied and constraints to inform other researchers in making improvements in the area of federated learning. The article addresses the importance of privacy-enhancing technology, such as differential privacy (DP), homomorphic encryption (HE), and secure multiparty computation (SMPC) in federated learning as they can achieve privacy as well as effectiveness in terms of communication efficiency and the cost of computation. The article examines federated learning applications in the privacy-sensitive field of natural language processing (NLP) and healthcare, as well as in the Internet of Things (IoT) and edge computing. We think that our contribution is a new one because it determines privacy evaluation metrics and highlights the measures according to the data privacy and correctness, cost of communication, cost of computation and scalability. Moreover, it presents an emergent need and offers prospective research areas of the federated learning field.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ammar Ahmed, Syed Muhammad Rizwan, Fasiha Ikram, Nasar Ahmed , Hamayun Khan , Muhammad Muhammad Zulkifl Hasan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.






