Impact of Sensory Branding and Brand Awareness on Consumer Buying Behavior
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62019/vsk6m466Keywords:
Sensory Branding, Brand Awareness, Consumer Buying Behavior, Perceived Quality, Brand Loyalty, Digital Branding StrategiesAbstract
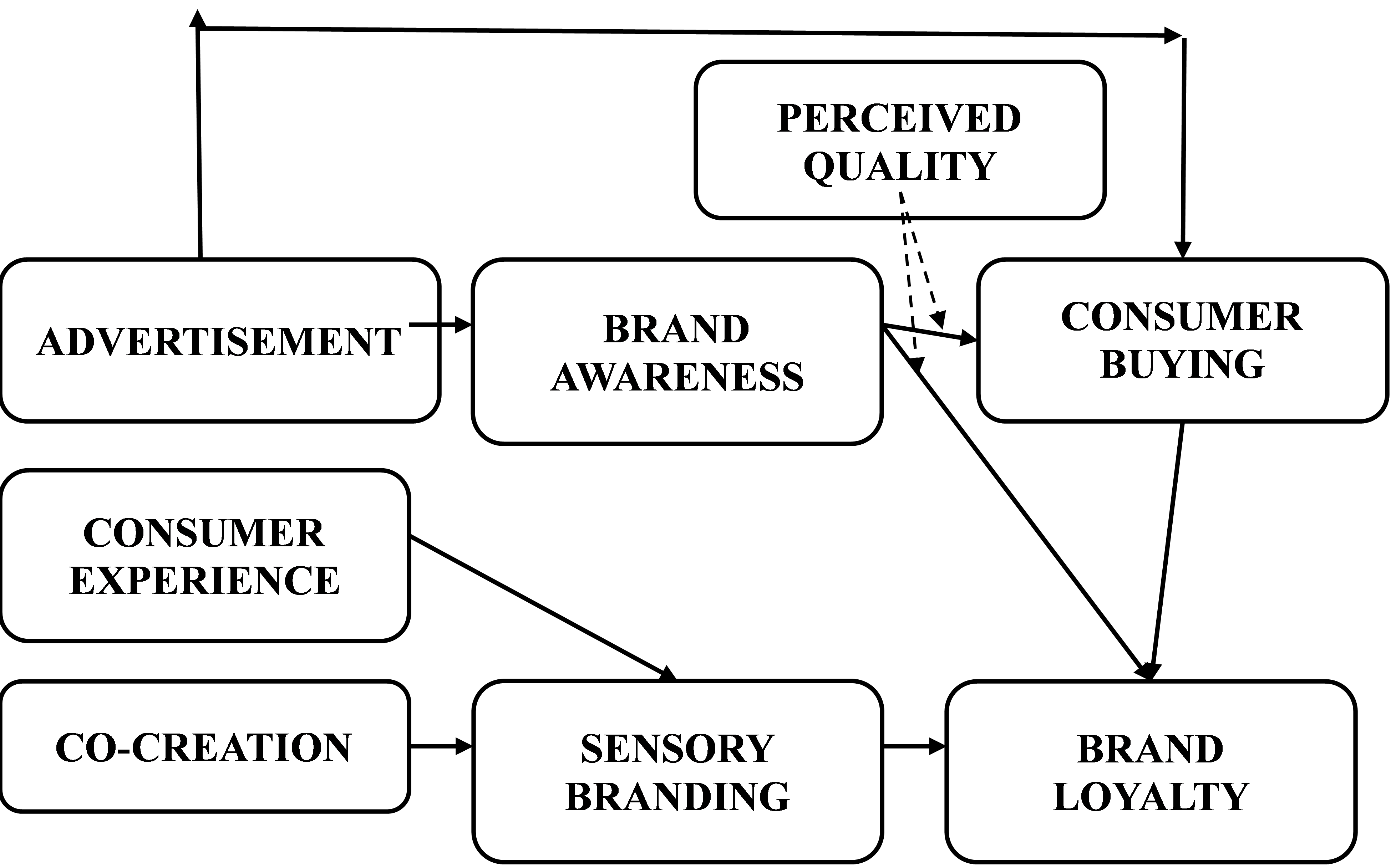
Consumer buying behavior is significantly influenced by branding strategies, particularly sensory branding and brand awareness. This study explores the impact of sensory branding and brand awareness on consumer purchasing decisions, emphasizing the mediating role of perceived quality and the moderating effect of consumer experience. The research adopts a quantitative approach, utilizing Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) to analyze survey data from consumers who have engaged with brand advertisements and sensory marketing efforts. Findings indicate that while advertisements enhance brand awareness, they do not directly lead to brand loyalty, challenging traditional marketing assumptions. Sensory branding significantly improves perceived quality, reinforcing its role in shaping consumer perceptions. However, perceived quality alone does not guarantee long-term loyalty, highlighting the necessity of emotional engagement and personalized consumer experiences. The study contributes to branding literature by integrating theoretical models such as the Stimulus-Organism-Response (SOR) framework and Aaker’s Brand Equity Model, providing insights into how brand awareness, sensory engagement, and perceived quality interact in consumer decision-making. Practical implications suggest that businesses should move beyond traditional advertising strategies to focus on multi-sensory engagement, consumer co-creation, and personalized branding experiences. Future research should further explore emotional branding and digital consumer engagement strategies to strengthen long-term brand loyalty. Using Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM), the study analyzed data from 350 respondents, revealing that brand awareness explains 23.6% of the variance (R² = 0.236), while consumer buying behavior is influenced by advertisement (β = 0.407, p < 0.001) and brand awareness (β = 0.087, p < 0.047). Furthermore, the study found that brand loyalty accounts for 35.9% of variance (R² = 0.359), with advertisement significantly contributing to brand loyalty (β = 0.420, p < 0.001)
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Sohaib Uz Zaman, Maryam Tahir, Syed Hasnain Alam, Muhammad Furqan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.






